Product Description
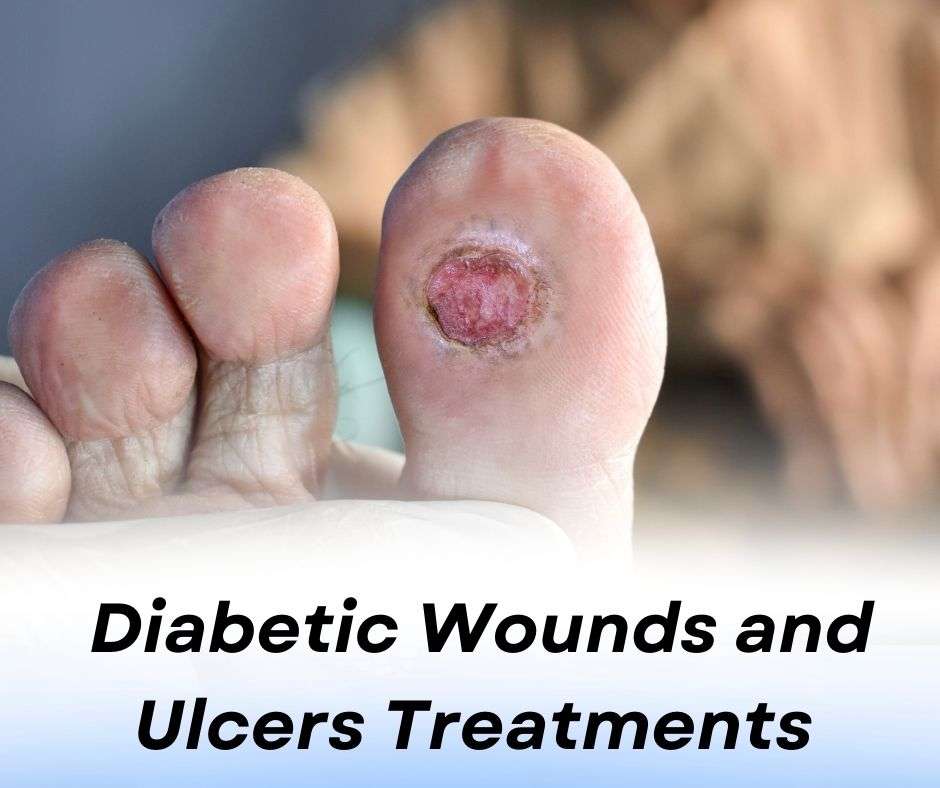
Diabetic Wounds and Ulcers – Dr. Uday Ravi
Diabetic wounds and ulcers are common complications for individuals with diabetes, particularly those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels. These conditions are often linked to the reduced ability of the body to heal wounds, and they can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the feet and legs.
Diabetes affects the body's ability to heal wounds due to a combination of factors, including poor circulation, neuropathy (nerve damage), and a weakened immune system. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, which makes it harder for wounds to heal. Additionally, neuropathy can cause a loss of sensation in the feet, meaning that people may not feel the initial signs of a wound or infection, allowing it to progress unnoticed.
Types of Diabetic Wounds and Ulcers:
Neuropathic ulcers: These are typically caused by nerve damage and occur on the feet, often on pressure points.
Ischemic ulcers: Result from poor blood circulation and typically form on the toes, heels, and lower legs.
Mixed ulcers: A combination of both neuropathy and poor circulation.
Symptoms of Diabetic Wounds and Ulcers:
Redness, swelling, or warmth around the wound.
Pain or tenderness in the affected area.
Formation of a blister, open sore, or ulcer that doesn’t heal.
Drainage or discharge from the wound, which may have an unpleasant odor.
Prevention and Treatment:
Regular Foot Care: Diabetics should inspect their feet daily for cuts, blisters, or signs of infection.
Proper Wound Care: Immediate cleaning and dressing of wounds are essential to prevent infection. If left untreated, diabetic wounds can become severely infected and may lead to complications such as gangrene or amputation.
Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing complications, including diabetic ulcers.
Medical Intervention: In cases of severe or non-healing wounds, a healthcare professional may recommend advanced wound care techniques, such as debridement, dressings, or even surgical procedures.
It’s essential for people with diabetes to consult a healthcare provider regularly and follow an appropriate treatment plan to manage diabetic wounds and ulcers effectively. Early detection and proper care can significantly improve healing outcomes.
Terms & conditions
Tags
#Diabetic wounds treatment in Bangalore
#Diabetic ulcers care in Bangalore
#Best treatment for diabetic wounds Bangalore
#Diabetic foot ulcer treatment in Bangalore
#Effective diabetic wound healing Bangalore
#Advanced treatment for diabetic ulcers in Bangalore
#Diabetic wound specialist in Bangalore
#Painless diabetic ulcer treatment Bangalore
#Diabetic foot care Bangalore
#Top diabetic wound care clinic Bangalore
#Best doctor for diabetic wounds in Bangalore
#Diabetic wound management in Bangalore
#Diabetic foot ulcer care Bangalore
#Non-healing diabetic wounds treatment in Bangalore
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Bangalore
#Diabetic wound healing clinic in Bangalore
#Diabetic wound treatment near me Bangalore
#Top diabetic ulcer specialists in Bangalore
#Healing diabetic ulcers in Bangalore
#Affordable diabetic wound treatment Bangalore
#Diabetic ulcers specialist doctor Bangalore
#Diabetic wound care center in Bangalore
#Diabetic wounds treatment in Whitefield
#Diabetic ulcers care in Koramangala
#Diabetic wound care in Indiranagar
#Foot ulcer treatment for diabetics in Jayanagar
#Diabetic ulcer care in HSR Layout
#Diabetic wound care in Rajajinagar
#Diabetic ulcers specialist in BTM Layout
#Foot ulcer care for diabetics in Marathahalli
#Diabetic wound management in Yelahanka
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Basavanagudi
#Diabetic foot care in Malleshwaram
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Electronic City
#Diabetic wound specialist in Vijayanagar
#Diabetic foot care in Hebbal
#Diabetic ulcer clinic in KR Puram
#Wound care for diabetics in Nagarbhavi
#Diabetic foot care in Sarjapur Road
#Ulcer treatment for diabetics in Banashankari
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in JP Nagar
#Diabetic wound healing clinic in Domlur
#Diabetic ulcers specialist in Hennur
#Diabetic wound care in Bellandur
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Frazer Town
#Diabetic wound care in MG Road
#Diabetic ulcers management in Richmond Town
#Diabetic foot ulcer care in Ulsoor
#Diabetic wound treatment in Kumaraswamy Layout
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Bommanahalli
#Diabetic wound care in Sahakar Nagar
#Diabetic foot ulcer treatment in Sadashivanagar
#Diabetic wound healing in Shantinagar
#Foot ulcer treatment for diabetics in VV Puram
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Kalasipalya
#Diabetic wound care in Chamarajpet
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Cottonpet
#Diabetic wound care in Palace Guttahalli
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Gandhinagar
#Foot ulcers treatment for diabetics in Majestic
#Diabetic wound care in RT Nagar
#Diabetic foot treatment in Jeevanbheemanagar
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Cox Town
#Diabetic wound care in Kasturi Nagar
#Foot ulcer treatment in Banaswadi
#Diabetic wound care in Doddanekkundi
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Mahadevapura
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Kadubeesanahalli
#Foot ulcer care in Banerghatta Road
#Diabetic ulcer care in Magadi Road
#Diabetic foot treatment in Peenya
#Diabetic wound care in Tumkur Road
#Diabetic ulcer specialist in Devanahalli
#Diabetic foot ulcer treatment in Hennur Bande
#Diabetic wound care in Kannuru
#Foot ulcer treatment in K R Puram
#Diabetic ulcer healing in Hoodi
#Diabetic wound care in Seegehalli
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Kadugodi
#Diabetic foot treatment in Whitefield
#Diabetic ulcers care in Varthur
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Balagere
#Foot ulcer care for diabetics in Gunjur
#Diabetic wound healing in Carmelaram
#Diabetic foot treatment in Sarjapura
#Diabetic ulcers care in Doddakannelli
#Diabetic wound healing in Kaikondrahalli
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Harlur
#Diabetic foot ulcer care in HSR Layout
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Kasavanahalli
#Foot ulcer treatment in Kudlu Gate
#Diabetic wound care in Singasandra
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Begur
#Diabetic ulcers care in Bommasandra
#Diabetic wound treatment in Electronic City
#Diabetic ulcer care in Jigani
#Diabetic wound treatment in Anekal
#Diabetic ulcer care in Bannerghatta
#Diabetic ulcer treatment in Hulimavu
#Diabetic wound healing in Arekere
#Diabetic foot care in Sarjapura
#Diabetic ulcers treatment in Doddakannelli